Because science makes your guns work and the more you know the greater your ability to understand science becomes. I do these for a select group of 400 people already so it is no problem for me to copy and post them here too. They are all multiple choice or true or false questions and range from astrophysics to zoology. They also vary greatly in difficulty since someone can be very knowledgable about chemistry and know very little about biology. The answer is always given below the options with an explanation and link for more information.
So with that said here is todays trivia.
------------------------------------------------
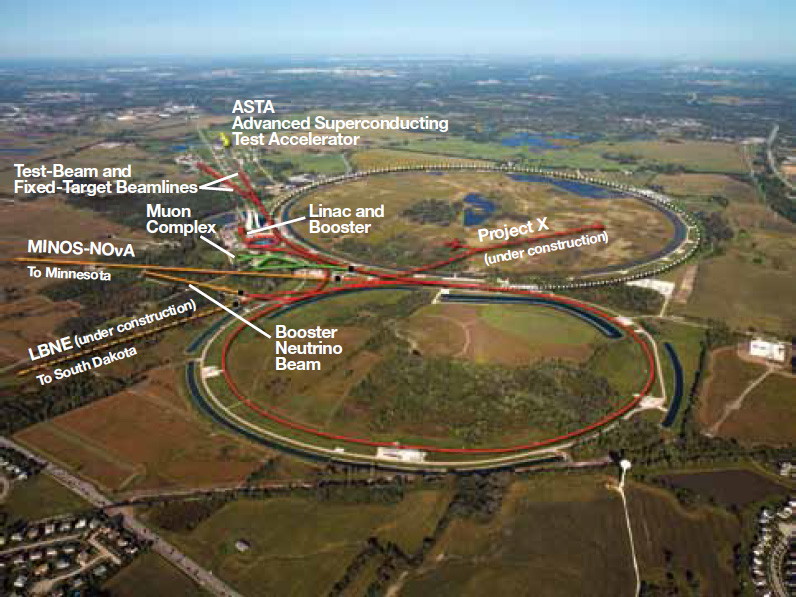
12-2-17 trivia. Pictured below is what should be a famous scientific laboratory and I have been there! What is name of the facility where it is located?
A. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Tennessee
B. Brookhaven National Laboratory, NY
C. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Washington
D. Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (FNAL) Batavia, Illinois.

-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
C. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Washington
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory is also called the Hanford site by most people. ;-)
Beyond PNNL, the National Science Foundation's LIGO, or the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory, also is right here in Richland. LIGO's mission is to observe gravitational waves of cosmic origin. Some of its research aims to unravel mysteries surrounding the formation of black holes and the birth of the universe.
Later this month, I look forward to helping celebrate the installation of advanced gravitational wave detectors at LIGO. The new instruments will enable even more advanced research because they are more sensitive and significantly increase the volume of space that LIGO will survey.
The Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) is designed to open the field of gravitational-wave astrophysics through the direct detection of gravitational waves predicted by Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity. LIGO’s multi-kilometer-scale gravitational wave detectors use laser interferometry to measure the minute ripples in space-time caused by passing gravitational waves from cataclysmic cosmic sources such as the mergers of pairs of neutron stars or black holes, or by supernovae. LIGO consists of two widely separated interferometers within the United States—one in Hanford, Washington and the other in Livingston, Louisiana—operated in unison to detect gravitational waves.
So with that said here is todays trivia.
------------------------------------------------
12-2-17 trivia. Pictured below is what should be a famous scientific laboratory and I have been there! What is name of the facility where it is located?
A. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Tennessee
B. Brookhaven National Laboratory, NY
C. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Washington
D. Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (FNAL) Batavia, Illinois.

-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
C. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Washington
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory is also called the Hanford site by most people. ;-)
Beyond PNNL, the National Science Foundation's LIGO, or the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory, also is right here in Richland. LIGO's mission is to observe gravitational waves of cosmic origin. Some of its research aims to unravel mysteries surrounding the formation of black holes and the birth of the universe.
Later this month, I look forward to helping celebrate the installation of advanced gravitational wave detectors at LIGO. The new instruments will enable even more advanced research because they are more sensitive and significantly increase the volume of space that LIGO will survey.
The Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) is designed to open the field of gravitational-wave astrophysics through the direct detection of gravitational waves predicted by Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity. LIGO’s multi-kilometer-scale gravitational wave detectors use laser interferometry to measure the minute ripples in space-time caused by passing gravitational waves from cataclysmic cosmic sources such as the mergers of pairs of neutron stars or black holes, or by supernovae. LIGO consists of two widely separated interferometers within the United States—one in Hanford, Washington and the other in Livingston, Louisiana—operated in unison to detect gravitational waves.