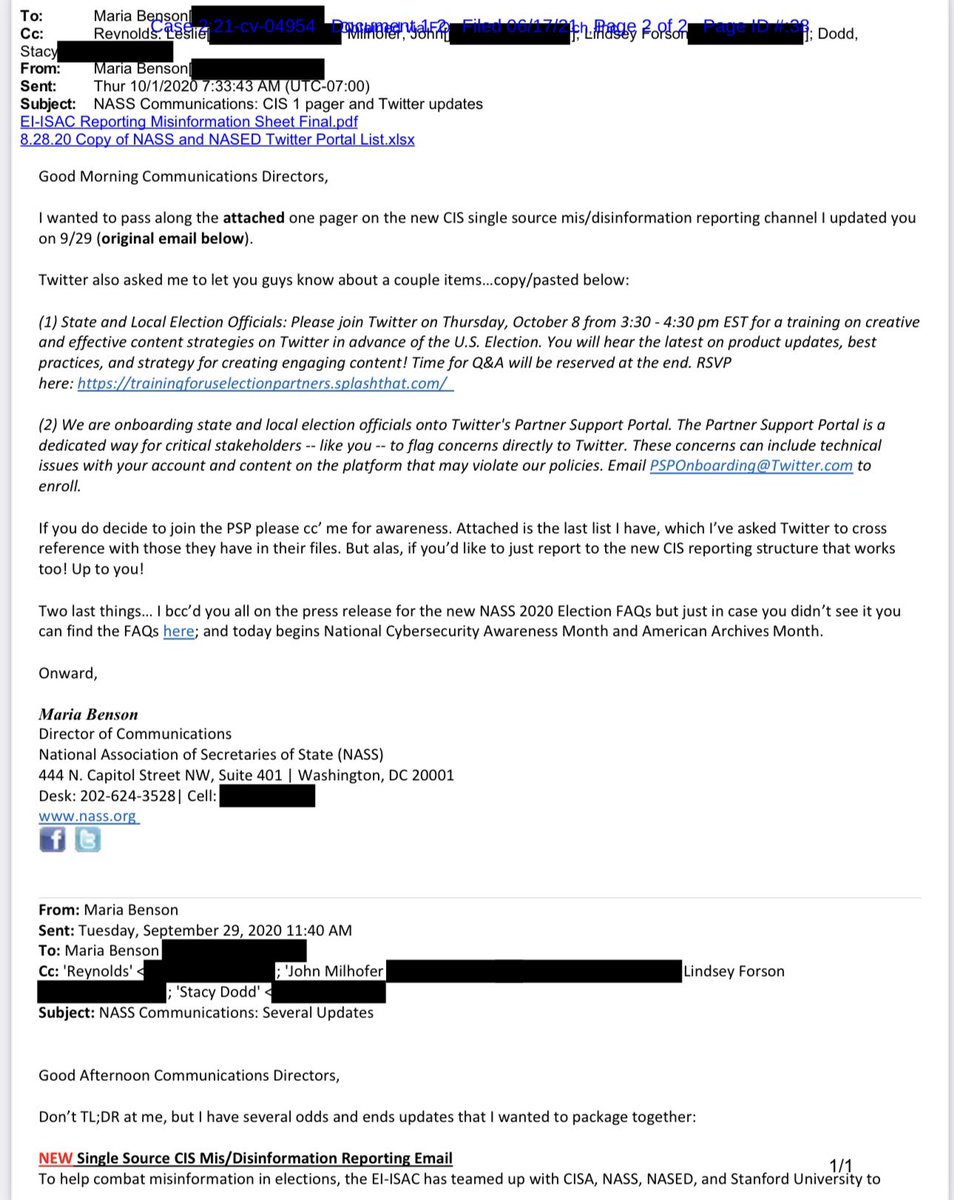
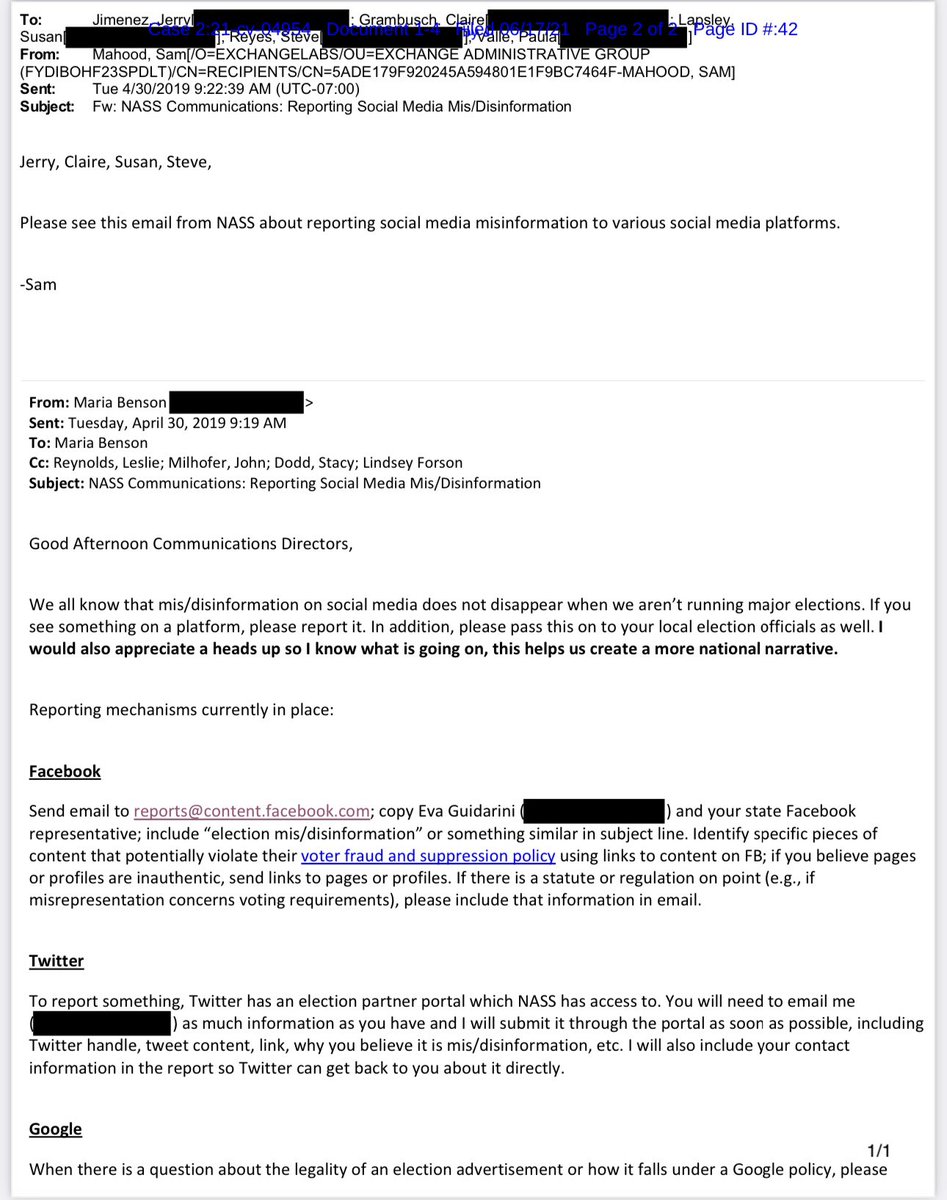
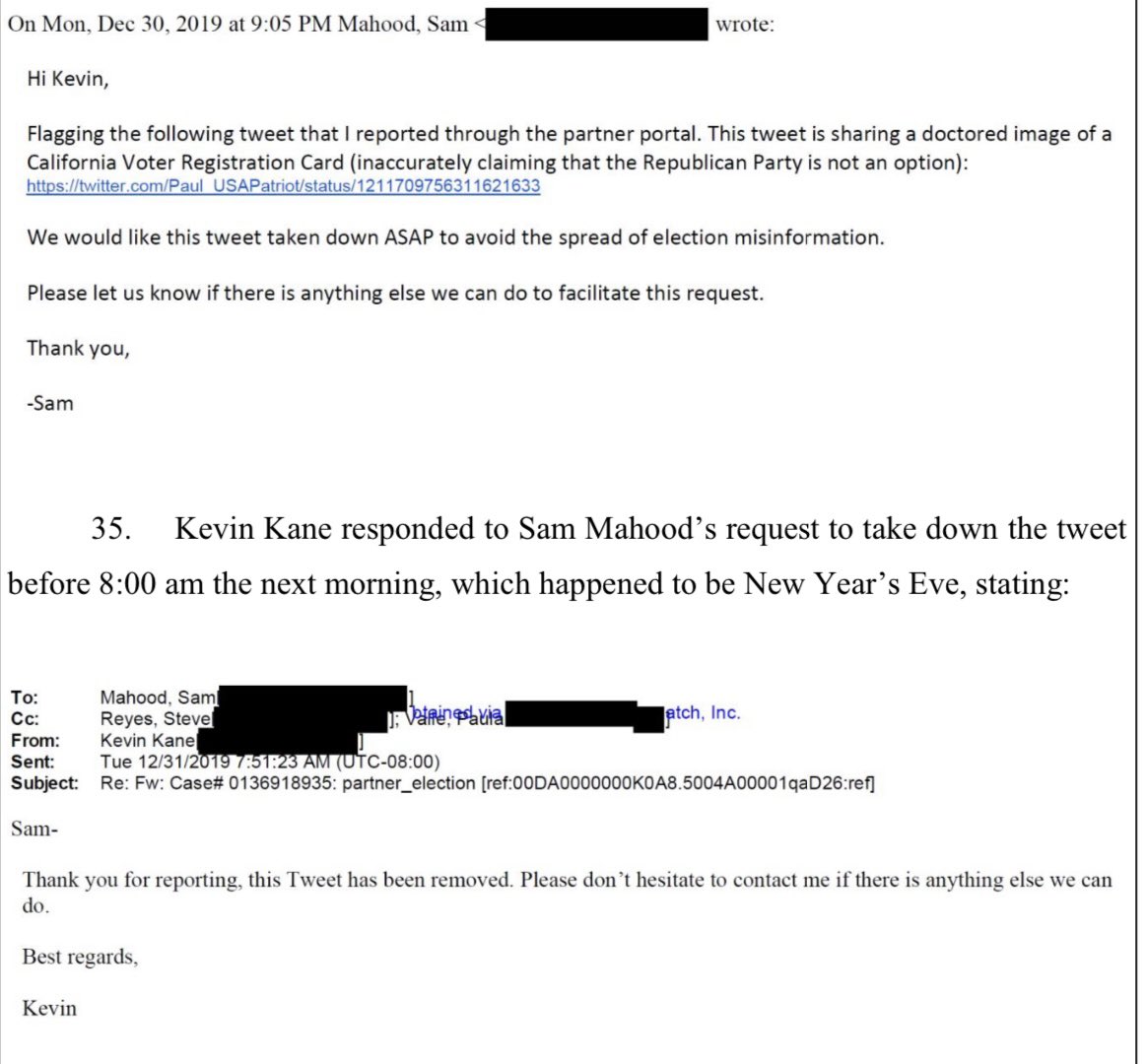
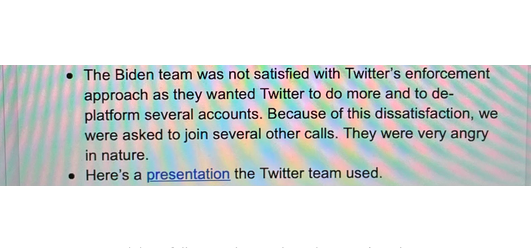
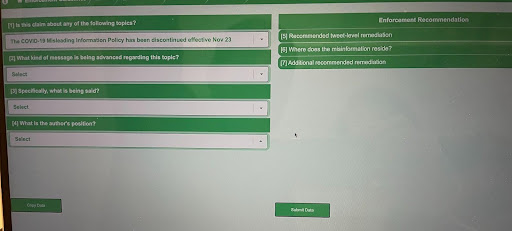
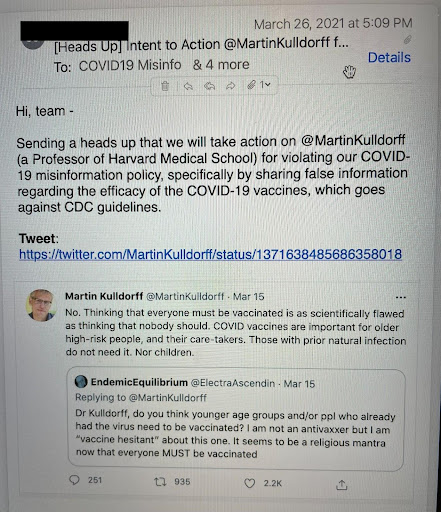
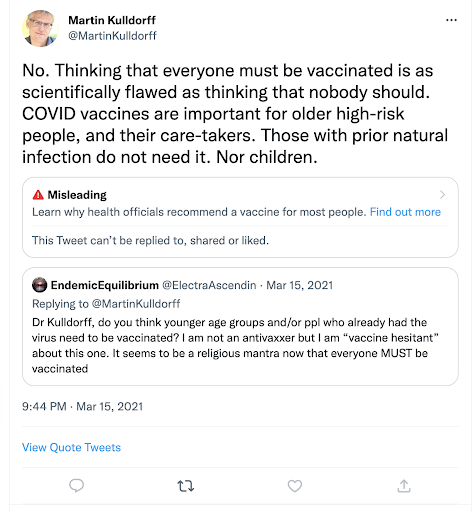
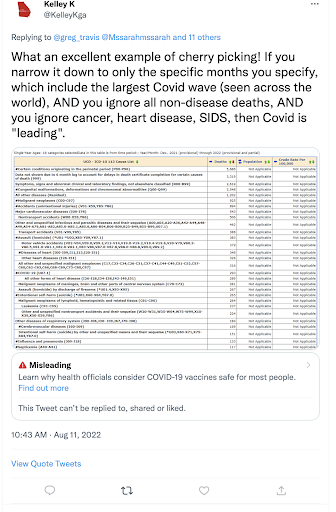
25. In Aug, 2020, FBI’s Chan asks Twitter: does anyone there have top secret clearance?
When someone mentions Jim Baker, Chan responds, "I don't know how I forgot him" — an odd claim, given Chan's job is to monitor Twitter, not to mention that they worked together at the FBI.
26. Who is Jim Baker? He's former general counsel of the FBI (2014-18) & one of the most powerful men in the U.S. intel community.
Baker has moved in and out of government for 30 years, serving stints at CNN, Bridgewater (a $140 billion asset management firm) and Brookings
27. As general counsel of the FBI, Baker played a central role in making the case internally for an investigation of Donald Trump
wsj.com/articles/fbi-t…
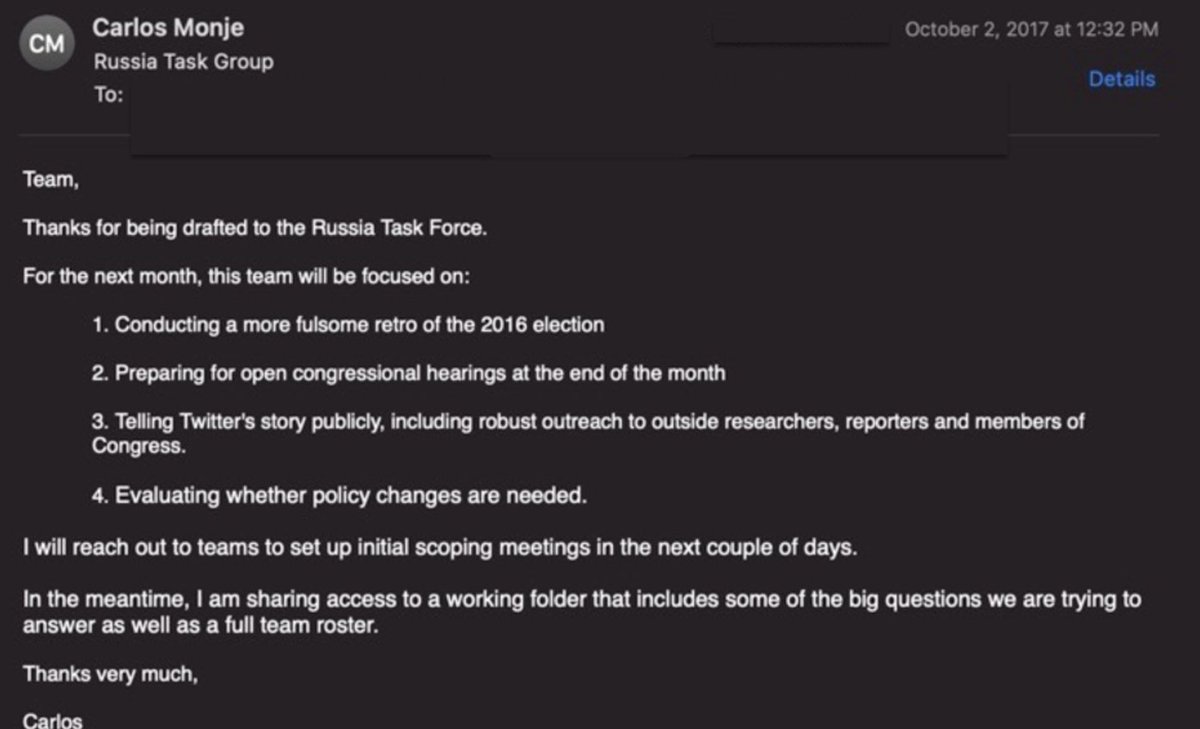
28. Baker wasn't the only senior FBI exec. involved in the Trump investigation to go to Twitter.
Dawn Burton, the former dep. chief of staff to FBI head James Comey, who initiated the investigation of Trump, joined Twitter in 2019 as director of strategy.
29. As of 2020, there were so many former FBI employees — "Bu alumni" — working at Twitter that they had created their own private Slack channel and a crib sheet to onboard new FBI arrivals.
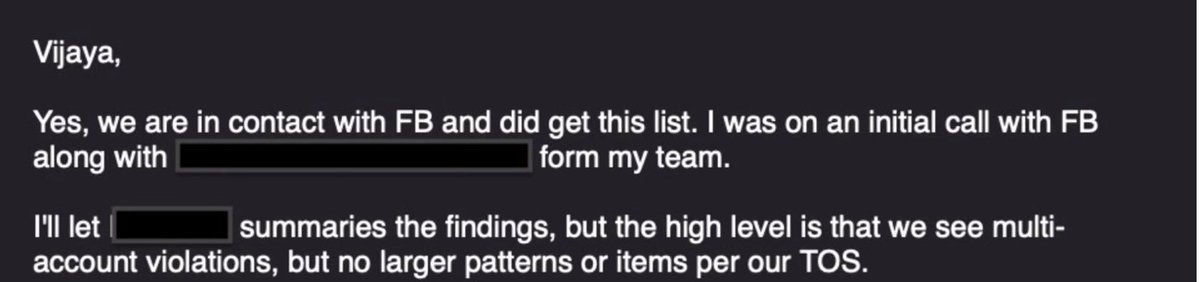
30. Efforts continued to influence Twitter's Yoel Roth.
In Sept 2020, Roth participated in an Aspen Institute “tabletop exercise” on a potential "Hack-and-Dump" operation relating to Hunter Biden
The goal was to shape how the media covered it — and how social media carried it
31. The organizer was Vivian Schiller, the fmr CEO of NPR, fmr head of news at Twitter; fmr Gen. mgr of NY Times; fmr Chief Digital Officer of NBC News
Attendees included Meta/FB's head of security policy and the top nat. sec. reporters for
@nytimes @wapo and others
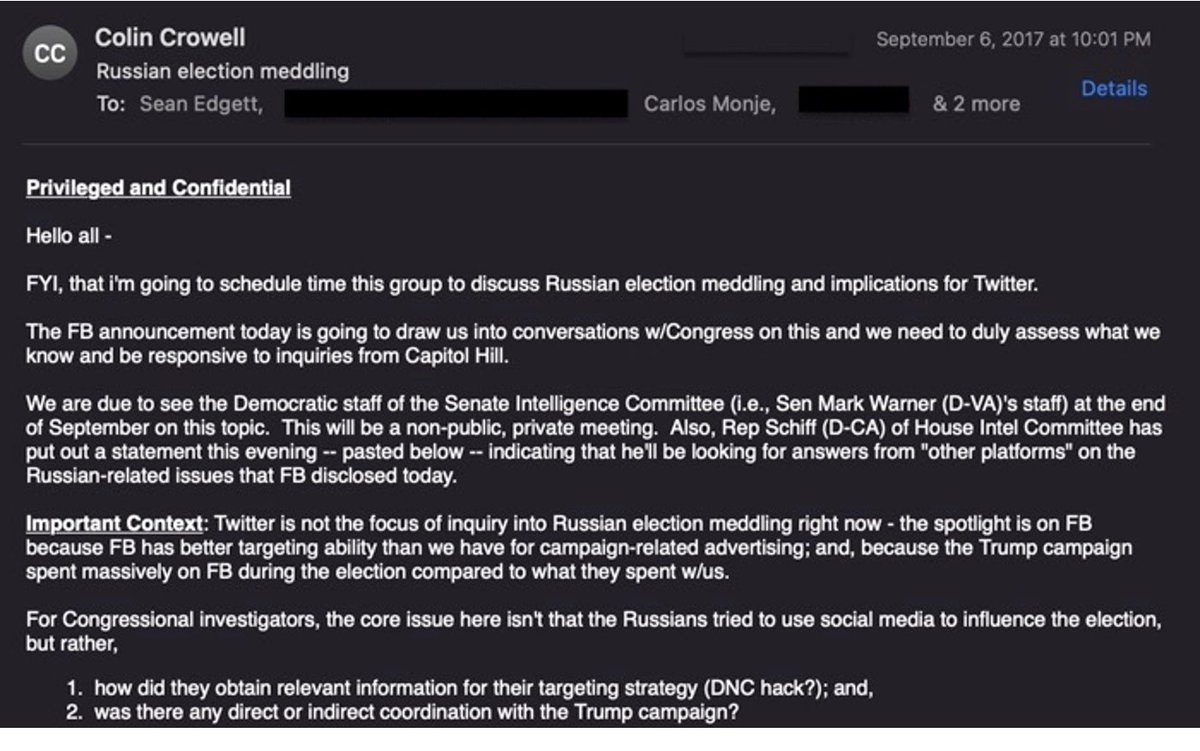
32. By mid-Sept, 2020, Chan & Roth had set up an encrypted messaging network so employees from FBI & Twitter could communicate.
They also agree to create a “virtual war room” for “all the [Internet] industry plus FBI and ODNI” [Office of the Director of National Intelligence].
33. Then, on Sept 15, 2020 the FBI’s Laura Dehmlow, who heads up the Foreign Influence Task Force, and Elvis Chan, request to give a classified briefing for Jim Baker, without any other Twitter staff, such as Yoel Roth, present.
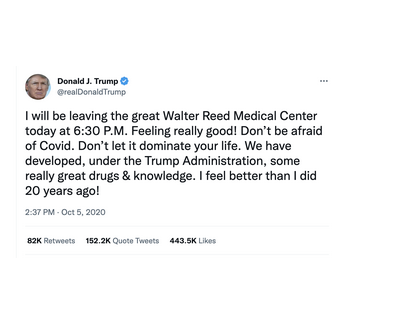
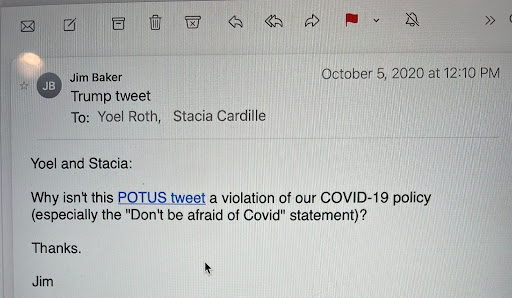
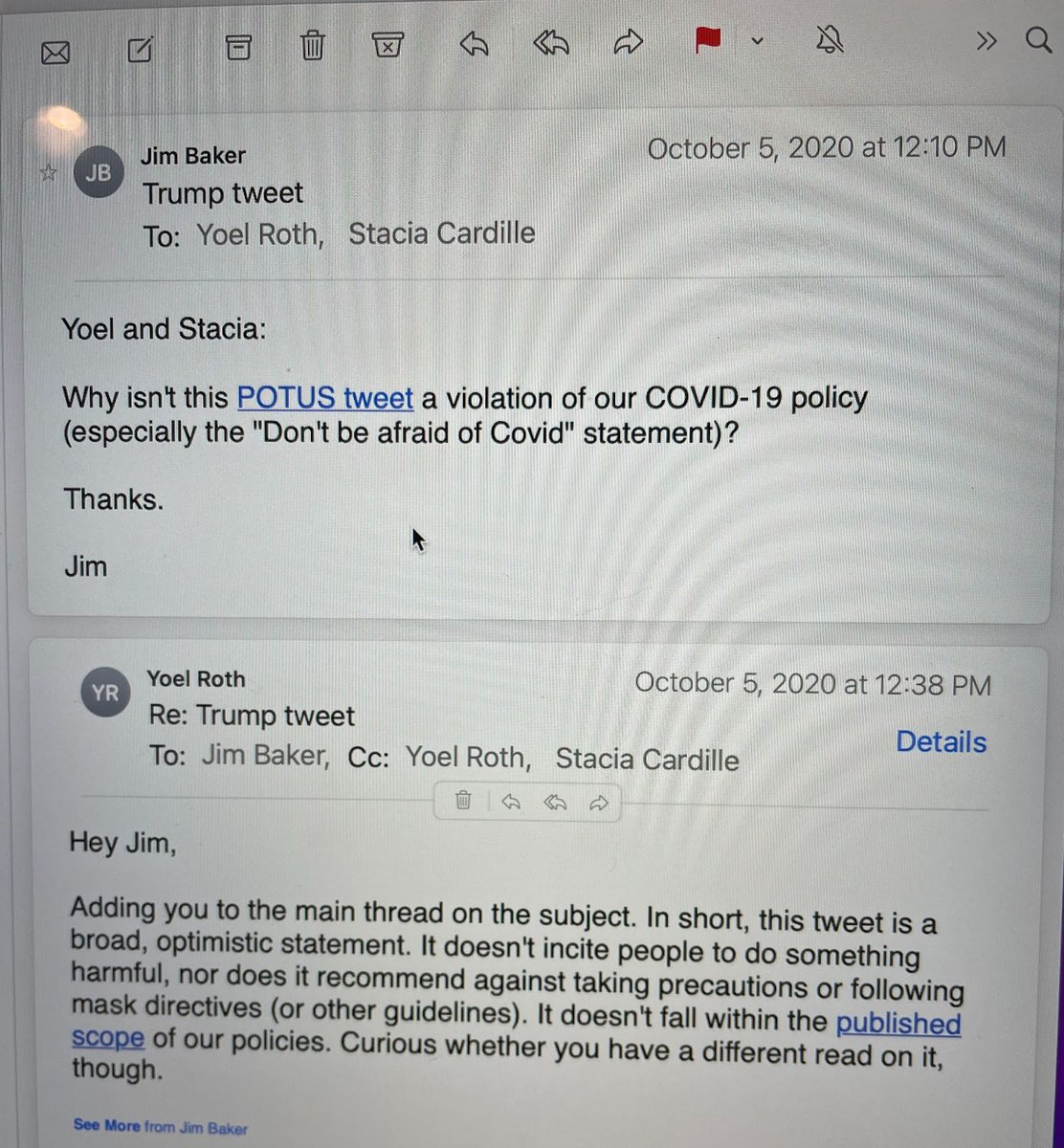
34. On Oct 14, shortly after
@nypost publishes its Hunter Biden laptop story, Roth says, “it isn’t clearly violative of our Hacked Materials Policy, nor is it clearly in violation of anything else," but adds, “this feels a lot like a somewhat subtle leak operation.”
35. In response to Roth, Baker repeatedly insists that the Hunter Biden materials were either faked, hacked, or both, and a violation of Twitter policy. Baker does so over email, and in a Google doc, on October 14 and 15.
36. And yet it's inconceivable Baker believed the Hunter Biden emails were either fake or hacked. The
@nypost had included a picture of the receipt signed by Hunter Biden, and an FBI subpoena showed that the agency had taken possession of the laptop in December 2019.
37. As for the FBI, it likely would have taken a few *hours* for it to confirm that the laptop had belonged to Hunter Biden. Indeed, it only took a few days for journalist
@peterschweizer to prove it.
38. By 10 am, Twitter execs had bought into a wild hack-and-dump story
“The suggestion from experts - which rings true - is there was a hack that happened separately, and they loaded the hacked materials on the laptop that magically appeared at a repair shop in Delaware”
39. At 3:38 pm that same day, October 14, Baker arranges a phone conversation with Matthew J. Perry in the Office of the General Counsel of the FBI
40. The influence operation persuaded Twitter execs that the Hunter Biden laptop did *not* come from a whistleblower.
One linked to a Hill article, based on a WaPo article, from Oct 15, which falsely suggested that Giuliani’s leak of the laptop had something to do with Russia.
41. There is evidence that FBI agents have warned elected officials of foreign influence with the primary goal of leaking the information to the news media. This is a political dirty trick used to create the perception of impropriety.
42. In 2020, the FBI gave a briefing to Senator Grassley and Johnson, claiming evidence of “Russian interference” into their investigation of Hunter Biden.
The briefing angered the Senators, who say it was done to discredit their investigation.
grassley.senate.gov/imo/media/doc/…
43. “The unnecessary FBI briefing provided the Democrats and liberal media the vehicle to spread their false narrative that our work advanced Russian disinformation.”
44. Notably, then-FBI General Counsel Jim Baker was investigated *twice,* in 2017 and 2019, for leaking information to the news media.
“You’re saying he’s under criminal investigation? That’s why you’re not letting him answer?” Meadows asked.
“Yes”
politico.com/story/2019/01/…
45. In the end, the FBI's influence campaign aimed at executives at news media, Twitter, & other social media companies worked: they censored & discredited the Hunter Biden laptop story.
By Dec. 2020, Baker and his colleagues even sent a note of thanks to the FBI for its work.
46. The FBI’s influence campaign may have been helped by the fact that it was paying Twitter millions of dollars for its staff time.
“I am happy to report we have collected $3,415,323 since October 2019!” reports an associate of Jim Baker in early 2021.
47. And the pressure from the FBI on social media platforms continues
In Aug 2022, Twitter execs prepared for a meeting with the FBI, whose goal was “to convince us to produce on more FBI EDRs"
EDRs are an “emergency disclosure request,” a warrantless search.
In response to the Twitter Files revelation of high-level FBI agents at Twitter,
@Jim_Jordan said, “I have concerns about whether the government was running a misinformation operation on We the People.”
nypost.com/2022/12/17/twi…
Anyone who reads the Twitter Files, regardless of their political orientation, should share those concerns.
/END